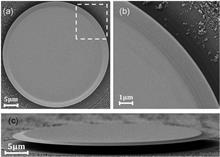
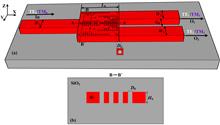
We demonstrate single-mode microdisk lasers in the telecom band with ultralow thresholds on erbium-ytterbium co-doped thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN). The active microdisk was fabricated with high-Q factors by photolithography-assisted chemomechanical etching. Thanks to the erbium-ytterbium co-doping providing high optical gain, the ultralow loss nanostructuring, and the excitation of high-Q coherent polygon modes, which suppresses multimode lasing and allows high spatial mode overlap between pump and lasing modes, single-mode laser emission operating at 1530 nm wavelength was observed with an ultralow threshold, under a 980-nm-band optical pump. The threshold was measured as low as 1 µW, which is one order of magnitude smaller than the best results previously reported in single-mode active TFLN microlasers. The conversion efficiency reaches 4.06 × 10-3, which is also the highest value reported in single-mode active TFLN microlasers.
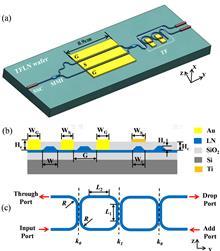
We propose and demonstrate an integrated microwave photonic sideband selector based on the thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) platform by integrating an electro-optic Mach–Zehnder modulator (MZM) and a thermo-optic tunable flat-top microring filter. The sideband selector has two functions: electro-optic modulation of wideband RF signal and sideband selection. The microwave photonic sideband selector supports processing RF signals up to 40 GHz, with undesired sidebands effectively suppressed by more than 25 dB. The demonstrated device shows great potential for TFLN integrated technology in microwave photonic applications, such as mixing and frequency measurement.
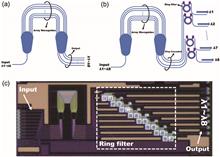
The silicon-based arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) is widely used due to its compact footprint and its compatibility with the mature CMOS process. However, except for AWGs with ridged waveguides of a few micrometers of cross section, any small process error will cause a large phase deviation in other AWGs, resulting in an increasing cross talk. In this paper, an ultralow cross talk AWG via a tunable microring resonator (MRR) filter is demonstrated on the SOI platform. The measured insertion loss and minimum adjacent cross talk of the designed AWG are approximately 3.2 and -45.1 dB, respectively. Compared with conventional AWG, its cross talk is greatly reduced.
Integrated optical gyroscopes (IOGs) have been an efficient tool for numerous applications in various fields, including inertial navigation, flight control, and earthquake monitoring. Here, we review the progress of integrated optical gyroscopes based on two categories of integrated interferometric optical gyroscopes (IIOGs) and integrated resonant optical gyroscopes (IROGs).
A polarization-insensitive mode-order converting power splitter using a pixelated region is presented and investigated in this paper. As TE0 and TM0 modes are injected into the input port, they are converted into TE1 and TM1 modes, which evenly come out from the two output ports. The finite-difference time-domain method and direct-binary-search optimization algorithm are utilized to optimize structural parameters of the pixelated region to attain small insertion loss, low crosstalk, wide bandwidth, excellent power uniformity, polarization-insensitive property, and compact size. Experimental results reveal that the insertion loss, crosstalk, and power uniformity of the fabricated device at 1550 nm are 0.57, -19.67, and 0.094 dB in the case of TE polarization, while in the TM polarization, the relevant insertion loss, crosstalk, and power uniformity are 0.57, -19.40, and 0.11 dB. Within a wavelength range from 1520 to 1600 nm, for the fabricated device working at TE polarization, the insertion loss, crosstalk, and power uniformity are lower than 1.39, -17.64, and 0.14 dB. In the case of TM polarization, we achieved an insertion loss, crosstalk, and power uniformity less than 1.23, -17.62, and 0.14 dB.
Silicon waveguides typically exhibit optical anisotropy, which leads to polarization correlation and single-polarization operations. This consequently creates a demand for polarization-control devices. This paper introduces a CMOS-compatible O-band reconfigurable TE/TM polarization rotator comprising two symmetrical polarization rotator–splitters and phase shifters. This configuration enables dynamic conversion of any linear polarization to its quadratic equivalent. Experimental results indicate that the reconfigurable polarization rotator exhibits an insertion loss of less than 1.5 dB. Furthermore, the bandwidth for a polarization extinction ratio beyond 15 dB exceeds 60 nm.
Mode splitters that directly separate modes without changing their orders are highly promising to improve the flexibility of the mode-division multiplexing systems. In this paper, we design a high-performance mode splitter on the silicon-on-insulator platform with a compact footprint of 14 µm× 2.5 µm using an inverse design method based on shape optimization. The fabrication of this mode splitter requires only a single lithography step and exhibits good fabrication tolerances. The experimental results show that the proposed device exhibits state-of-the-art insertion loss (<0.9 dB) and cross talk (<-16 dB) over a broad bandwidth (1500–1600 nm). Furthermore, the shape optimization method used is implemented to design a dual-mode (de)multiplexer, and the experimental results fulfill the design objective, demonstrating the excellent generality of the design method in this paper.
A flexible-grid 1×(2×3) mode- and wavelength-selective switch which comprises counter-tapered couplers and silicon microring resonators has been proposed, optimized, and demonstrated experimentally in this work. By carefully thermally tuning phase shifters and silicon microring resonators, mode and wavelength signals can be independently and flexibly conveyed to any one of the output ports, and different bandwidths can be generated as desired. The particle swarm optimization algorithm and finite difference time-domain method are employed to optimize structural parameters of the two-mode (de)multiplexer and crossing waveguide. The bandwidth-tunable wavelength-selective optical router composed of 12 microring resonators is studied by taking advantage of the transfer matrix method. Measurement results show that, for the fabricated module, cross talk less than -10.18 dB, an extinction ratio larger than 17.41 dB, an in-band ripple lower than 0.79 dB, and a 3-dB bandwidth changing from 0.38 to 1.05 nm are obtained, as the wavelength-channel spacing is 0.40 nm. The corresponding response time is measured to be 13.64 µs.
Integrated diffractive optical neural networks (DONNs) have significant potential for complex machine learning tasks with high speed and ultralow energy consumption. However, the on-chip implementation of a high-performance optical neural network is limited by input dimensions. In contrast to existing photonic neural networks, a space-time interleaving technology based on arrayed waveguides is designed to realize an on-chip DONN with high-speed, high-dimensional, and all-optical input signal modulation. To demonstrate the performance of the on-chip DONN with high-speed space-time interleaving modulation, an on-chip DONN with a designed footprint of 0.0945 mm2 is proposed to resolve the vowel recognition task, reaching a computation speed of about 1.4×1013 operations per second and yielding an accuracy of 98.3% in numerical calculation. In addition, the function of the specially designed arrayed waveguides for realizing parallel signal inputs using space-time conversion has been verified experimentally. This method can realize the on-chip DONN with higher input dimension and lower energy consumption.
We propose and demonstrate a cryogenic thermo-optic (TO) modulator in x-cut thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) with an NbN superconducting heater. Compared to a conventional metal heating electrode, a fast and energy-efficient modulation is obtained by placing an NbN superconducting heating electrode above the TFLN waveguide. The transition of the NbN superconducting electrode between superconducting and normal states turns the heating and cooling processes from continuous to discontinuous change. Thus, the energy consumption during the modulation process is reduced proportionally. The rise/fall time of the proposed device is 22 µs/15 µs, which has been the fastest response time reported in TFLN thermo-optic modulators so far. The presented TO modulator can easily be used at cryogenic temperatures and has great potential for applications in cryogenic optoelectronics.
Interface states are widely applied in waveguide devices. However, previous studies failed to achieve photonic and phononic interface states independent of each other in the same crystal structure depending on the behavior of the crystal structure, i.e., photonic or phononic crystals, making the function of interface states single. In this study, straight-line and circular photonic and phononic interface states were realized independently in sunflower-type crystals. In addition, with a defect and a metal barrier, interface states could remain almost undamaged. The results have the potential to achieve multi-function devices and reduce the cost of engineering applications.
The microring resonator based on lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) is a promising platform for broadband nonlinearity process because of its strong second-order nonlinear coefficients, the capability of dispersion engineering, etc. It is important to control the energy transmitted into the resonator at different wavelengths, as this becomes difficult for two bands across an octave. In this Letter, we study the effect of different pulley bus-resonator configurations on phase mismatching and mode field overlap. We achieve the control of energy transmission coefficients at different wavebands simultaneously and provide a general design methodology for coupled structures for broadband applications. This paper can contribute to quantum and classical optical broadband applications based on LNOI microring resonators.
More durable (with high impact force), lighter, and more compact flexible azo dye micropolarizers are attractive candidates for low-cost, simple polarization imaging systems. The liquid crystal polymer (LCP), as an emerging material developed by photo-alignment technology, is a potential material for organizing the long-range ordered structure of azo dyes. However, little research has been done on LCP aligned azo dyes. This paper points out and solves a key problem that restricts the fabrication of high-precision arrays in guest (azo dye)-host (LCP) systems: the doping of dyes leads to disorder of the LCP during curing. After solving the problem, the relationship between the thickness of the LCP and the extinction ratio of the polarizing film was investigated, which effectively improved the extinction ratio. Alignment of azo dye molecules in the range of 2 µm (0°–180°) and arrays of micropolarizers (0°, 45°, 90°, -45°) with 8 µm × 8 µm pixel pitch was achieved by laser direct writing technology. The bending cycle test demonstrates the mechanical stability of the ultrathin flexible polarizer. The flexible patterned polarizer with robust chemical and mechanical stabilities provides a flexible way to capture the polarization of the light and highly integrated advanced flexible optoelectronic devices.
We propose a new type of dispersion-flattened waveguide without a slot-assisted structure that can obtain an ultra-flat group velocity dispersion profile with five or six zero-dispersion wavelengths in the mid-infrared region. The dispersion profile becomes less sensitive to the waveguide dimensions due to the absence of the slot-assisted structure, making waveguide fabrication more friendly. The dispersion profile varies between -0.472 and 0.365ps/(nm · km) over a 2665 nm bandwidth from 2885 nm to 5550 nm with a flatness of 3183.99 nm2 · km/ps. Two different combinations of materials are demonstrated for dispersion flattening of the proposed waveguide structures. We also provide design guidance for the proposed waveguide structures with other combinations of materials.
Based on the one-dimensional periodic and Fibonacci-like waveguide arrays, we experimentally investigate localized quantum walks (QWs), both in the linear and nonlinear regimes. Unlike the ballistic transport behavior in conventional random QWs, localization of QWs is obtained in the Fibonacci-like waveguide arrays both theoretically and experimentally. Moreover, we verify the enhancement of the localization through nonlinearity-induced effect. Our work provides a valid way to study localization enhancement in QWs, which might broaden the understanding of nonlinearity-induced behaviors in quasi-periodic systems.
A quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK) coherent photodetector chip consisting of a 4×4 multimode interference 90° optical hybrid and a four-channel evanescent photodetector array is designed and fabricated with its photo-response in the L-band characterized. The metal organic chemical vapor deposition regrowth method is adopted to realize active–passive monolithic integration. The chip exhibits a low dark current below 100 nA for each photodetector in the array, a low excess loss of 0.85 dB, a common mode ratio rejection better than 13.6 dB, and a phase deviation within ±10° over the 40 nm wavelength span.
We present a theoretical analysis of a novel multi-channel light amplification photonic system on chip, where the nonlinear Raman amplification phenomenon in the silicon (Si) wire waveguide is considered. Particularly, a compact and temperature insensitive Mach–Zehnder interferometer filter working as demultiplexer is also exploited, allowing for the whole Si photonic system to be free from thermal interference. The propagation of the multi-channel pump and Stokes lights is described by a rigorous theoretical model that incorporates all relevant linear and nonlinear optical effects, including the intrinsic waveguide optical losses, first- and second-order frequency dispersion, self-phase and cross-phase modulation, phase shift and two-photon absorption, free-carriers dynamics, as well as the inter-pulse Raman interaction. Notably, to prevent excessive drift of the transmission window of the demultiplexer caused by ambient temperature variations and high thermo-optical coefficient of Si, an asymmetric waveguide width is adopted in the upper and lower arms of each Mach–Zehnder interferometer lattice cell. A Chebyshev half-band filter is utilized to achieve a flat pass-band transmission, achieving a temperature sensitivity of 1.4 pm/K and over 100 K temperature span. This all-Si amplifier shows a thermally robust behavior, which is desired by future Si-on-insulator (SOI) applications.
Lithium niobate (LiNbO3, LN) channel and ridge waveguides have been successfully fabricated by He ion implantation, which has energy of 500 keV and fluence of 1.5×1016 ions/cm2 and is combined with lithography and the precise diamond dicing technique. The refractive index profile of the annealed LN planar waveguide was reconstructed. The propagation loss of the channel waveguide with a width of 10 µm and that of the ridge waveguides with widths of 25 µm and 15 µm were investigated by the end-face coupling method. In our work, the factors that affect the waveguide properties of channel and ridge waveguides were revealed.
We demonstrate an ultra-compact short-wave infrared (SWIR) multispectral detector chip by monolithically integrating the narrowband Fabry–Perot microcavities array with the InGaAs detector focal plane array. A 16-channel SWIR multispectral detector has been fabricated for demonstration. Sixteen different narrowband response spectra are acquired on a 64×64 pixels detector chip by four times combinatorial etching processes. The peak of the response spectra varies from 1450 to 1666 nm with full width at half-maximum of 24 nm on average. The size of the SWIR multispectral detection system is remarkably reduced to a 2 mm2 detector chip.
Photonic structures with topological edge states and resonance loops are both important in optical communication systems, but they are usually two separate structures. In order to obtain a photonic system combining properties from both, we design multiple-layer nested photonic topological structures. The nested topological loops not only have topological protection immune to structural disorder and defects, but also possess both the properties of unidirectional propagation and loop resonance. Through mode analysis and simulations, we find that the transport can form diverse circulation loops. Each loop has its own resonance frequencies and can be solely excited in the nested layered structure through choosing its resonance frequencies. As a result, this work shows great application prospects in the area of reconfigurable photonic circuits.
We designed and demonstrated experimentally a silicon photonics integrated dynamic polarization controller. The overall size of the dynamic polarization controller on chip is 2.830 mm×0.210 mm×1 mm. The modulation bandwidth is 30 kHz. By using a variable step simulated annealing approach, we achieve a dynamic polarization extinction ratio greater than 25 dB. A numerical simulation method was used to optimize the relevant parameters of the dynamic polarization controller. It is expected that the dynamic polarization controller can be utilized in fiber communication systems or silicon photonics integrated quantum communication systems to minimize the size and decrease the cost further.
The 4H-silicon carbide on insulator (4H-SiCOI) has recently emerged as an attractive material platform for integrated photonics due to its excellent quantum and nonlinear optical properties. Here, we experimentally realize one-dimensional photonic crystal nanobeam cavities on the ion-cutting 4H-SiCOI platform. The cavities exhibit quality factors up to 6.1×103 and mode volumes down to 0.63 × (λ/n)3 in the visible and near-infrared wavelength range. Moreover, by changing the excitation laser power, the fundamental transverse-electric mode can be dynamically tuned by 0.6 nm with a tuning rate of 33.5 pm/mW. The demonstrated devices offer the promise of an appealing microcavity system for interfacing the optically addressable spin defects in 4H-SiC.
We designed a tunable wavelength-selective quasi-resonant cavity enhanced photodetector (QRCE-PD) based on a high-contrast subwavelength grating (SWG). According to simulation results, its peak quantum efficiency is 93.2%, the 3 dB bandwidth is 33.5 GHz, the spectral linewidth is 0.12 nm, and the wavelength-tuning range is 28 nm (1536–1564 nm). The QRCE-PD contains a tunable Fabry–Perot (F-P) filtering cavity (FPC), a symmetrical SWG deflection reflector (SSWG-DR), and a built-in p-i-n photodiode. The FPC and the SSWG-DR form an equivalent multi-region F-P cavity together by multiple mutual mirroring, which makes the QRCE-PD a multi-region resonant cavity enhanced photodetector. But, QRCE-PD relies on the multiple-pass absorption enhanced effect to achieve high quantum efficiency, rather than the resonant cavity enhanced effect. This new photodetector structure is significant for the application in the dense wavelength division multiplexing systems.
Low-loss dielectric terahertz (THz) chips are efficient platforms for diverse THz applications. One of the key elements in the chip is the coupler. Most of the available THz couplers are in-plane and couple the THz wave from the metal waveguide to the dielectric waveguide. However, out-of-plane couplers are more suitable for wafer-scale testing and tolerant of alignment variation. In this work, we propose an out-of-plane THz coupler for coupling the antenna to the dielectric waveguide. The device is constructed using a grating and a compact spot-size converter. As the conventional optical spot-size converters that apply directly to THz chips are too large, we have designed a compact spot-size converter based on a tapered waveguide with a lens. The total device is 2.9 cm long and can couple a 7 mm diameter THz beam to a 500 µm wide waveguide. The device can scan the THz beam, radiate the input rectangular waveguide mode to free space, and drive the rotation angle of the fan beam through the scanning frequency. We fabricated the device using a single lithography step on a silicon wafer. The out-of-plane coupling efficiency was found to be ∼5 dB at 194 GHz. The fan-beam steering range was found to be around 40° in the frequency range of 170–220 GHz. The proposed out-of-plane coupling technique may provide an effective way for THz wafer-scale testing with a higher degree of freedom for on-chip integration. Also, the proposed technique being non-mechanical, beam steering using it, may therefore find applications in THz radar, communication, and sensing.
A 2-mm-long silicon-on-insulator grating emitter with a narrow angular full width at half-maximum (FWHM) and a high sideband suppression ratio (SSR) is proposed and designed. It consists of a Si3N4/Si grating with an approximate Gaussian emission profile along the grating length, which aims to reduce the sidelobe intensity of the scanning light in the far-field, thereby improving the resolution of the longitudinal steering resolution of the light detection and ranging (lidar). Numerical analysis shows that the angular FWHM of the emitted beam could be as low as 0.026° for a grating length of 2.247 mm and the input TE-like waveguide mode at 1550 nm, and the SSR could be more than 32.622 dB. Moreover, this Si3N4/Si grating exhibits a favorable fabrication error tolerance when considering the width and length variation of the Si3N4 overlayer in practice. Our design offers a promising platform for realizing integrated optical phased arrays for the long-distance solid-state lidar.
An effective way to fabricate high-quality (Q) silicon microcavities on-chip is proposed and studied. Our fabrication technique consists of two significant steps: (1) patterning a special silicon micro-pillar by Bosch processes and (2) subsequent reflow of the pillar into a spherical-like microcavity using a laser pulse at 532 nm. Its shape and surface roughness are characterized using a scanning electron microscope and an atomic force microscope. The root-mean-square roughness of the surface is about 0.6 nm. A representative value for the loaded Q-factors of our silicon spherical-like microcavities is on the order of 105.
We design and fabricate an unbalanced Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) via electron beam lithography and inductively coupled plasma etching on lithium niobate thin film. The single unbalanced MZI exhibits a maximum extinction ratio of 32.4 dB and a low extra loss of 1.14 dB at the telecommunication band. Furthermore, tunability of the unbalanced MZI by harnessing the thermo-optic and electro-optic effect is investigated, achieving a linear tuning efficiency of 42.8 pm/°C and 55.2 pm/V, respectively. The demonstrated structure has applications for sensing and filtering in photonic integrated circuits.
We report an electro-optically (EO) tunable microdisk laser fabricated on the erbium (Er3+)-doped lithium niobate on insulator (LNOI) substrate. By applying a variable voltage on a pair of integrated chromium (Cr) microelectrodes fabricated near the LNOI microdisk, electro-optic modulation with an effective resonance-frequency tuning rate of 2.6 GHz/100 V has been achieved. This gives rise to a tuning range of 45 pm when the electric voltage is varied between -200 V and 200 V.
Here, we designed a broadband, low loss, compact, and fabrication-tolerant silicon-based four-mode edge coupler, composed of a 1×3 adiabatic mode-evolution counter-taper splitter and a triple-tip inverse taper. Based on mode conversion and power splitting, the proposed structure can simultaneously realize efficient mode coupling from TE0, TM0, TE1, and TM1 modes of multimode silicon waveguides to linearly polarized (LP), LP01,x, LP01,y, LP11a,x, and LP11a,y, modes in the few-mode fiber. To the best of our knowledge, we proposed the first scheme of four LP modes coupling, which is fully compatible with standard fabrication process. The 3D finite-difference time-domain simulation results show that the on-chip conversion losses of the four modes remain lower than 0.62 dB over the 200 nm wavelength range, and total coupling losses are 4.1 dB, 5.1 dB, 2.1 dB, and 2.9 dB for TE0-to-LP01,x, TM0-to-LP01,y, TE1-to-LP11a,x, and TM1-to-LP11a,y, respectively. Good fabrication tolerance and relaxed critical dimensions make the four-mode edge coupler compatible with standard fabrication process of commercial silicon photonic foundries.
Based on the Vernier effect of the cascaded double ring resonator (CDRR) sensor, a sensor consisting of a microfluidic control system, a sensing ring, and a reference ring with a micro-heater for thermal tuning is proposed in this paper. In wavelength interrogation, a broadband spectrometer or a large tunable range laser is not required. The shift of the output spectrum caused by the refractive index change of the sample is converted into the change of the electric power by the thermal tuning heater. Due to the Vernier effect, the sensitivity of the sensor is 20 times higher than that of the single ring. The spectral envelope of the thermal-optic tuning of the sensor was fitted by a Gaussian function in the wavelength range of 8 nm. The experimental results showed that the sensitivity was 33.703 W/RIU, and the limit of detection was 1.34×10-5 RIU.
To overcome the capacity crunch of optical communications based on the traditional single-mode fiber (SMF), different modes in a few-mode fiber (FMF) can be employed for mode division multiplexing (MDM). MDM can also be extended to photonic integration for obtaining improved density and efficiency, as well as interconnection capacity. Therefore, MDM becomes the most promising method for maintaining the trend of “Moore’s law” in photonic integration and optical fiber transmission. In this tutorial, we provide a review of MDM works and cutting-edge progresses from photonic integration to optical fiber transmission, including our recent works of MDM low-noise amplification, FMF fiber design, MDM Si photonic devices, and so on. Research and application challenges of MDM for optical communications regarding long-haul transmission and short reach interconnection are discussed as well. The content is expected to be of important value for both academic researchers and industrial engineers during the development of next-generation optical communication systems, from photonic chips to fiber links.
Optical channel waveguides with depressed cladding configurations have been produced in Nd,Gd:CaF2 laser crystals by using ultrafast laser inscription. Waveguide properties are investigated in terms of guiding behaviors and localized laser-induced lattice damages. Under an optical pump of 808 nm light, continuous-wave waveguide lasing at 1.06 μm is achieved, with a single-mode operation and a minimum lasing threshold of 98.8 mW. Furthermore, the visible emissions of Nd3+ with short wavelengths ranging from 415 nm to 550 nm and long wavelengths from 550 nm to 625 nm are observed upon 808 nm laser excitation via the up-converted process. The intensity ratios of two wavelength ranges are proved to be tunable through changing the pumping polarizations.
As a promising spectral window for optical communication and sensing, it is of great significance to realize on-chip devices at the 2 µm waveband. The development of the 2 µm silicon photonic platform mainly depends on the performance of passive devices. In this work, the passive devices were fabricated in the silicon photonic multi-project wafer process. The designed micro-ring resonator with a 0.6 µm wide silicon ridge waveguide based on a 220 nm silicon-on-insulator platform achieves a high intrinsic quality factor of 3.0×105. The propagation loss is calculated as 1.62 dB/cm. In addition, the waveguide crossing, multimode interferometer, and Mach–Zehnder interferometer were demonstrated at 2 µm with good performances.
Efficiently tuning the output intensity of an optical device is of vital importance for the establishment of optical interconnects and networks. Thermo-optical modulation is an easily implemented and convenient approach and has been widely employed in photonic devices. In this paper, we proposed a novel thermo-optical modulator based on a microfiber knot resonator (MKR) and graphene heater. Upon applying voltage to graphene, the resonant property of the MKR could be thermally tuned with a maximum phase shift of 2.1π. Intensity modulation shows a fast optical response time thanks to the high thermal conductivity of graphene and the thin microfiber diameter of the MKR.
Electro-optic (EO) ring resonator modulators have a number of communications and scientific applications, including analog optical links, optical signal processing, and frequency comb generation. Among the EO materials used to fabricate ring modulators, the EO polymer has many promising characteristics, including a high EO coefficient of 100–200 pm/V (3–7 times larger than that of LiNbO3), an ultrafast EO response time (10 fs), a low dielectric constant (3 to 4) with very little dispersion up to at least 250 GHz, and a straightforward spin-coating fabrication process. These inherent characteristics will be able to combine excellent EO properties with simple processing in achieving exceptional performance in a variety of high-speed optical modulation and sensing devices. This review focuses on the research and recent development of ring resonator modulators based on EO polymers. The first part describes the operation principle of EO ring resonator modulators, such as modulation mechanism, EO tunability, and 3 dB bandwidth. Subsequently, the emphasis is placed on the discussion of the ring modulators with EO polymers as the waveguide core and the improvement of EO modulation by using an EO polymer/titanium dioxide hybrid core. At the end, a series of EO polymers on silicon platforms including slot modulators, etching-free modulators, and athermal modulators are reviewed.
Copper (Cu) nanoparticles (NPs) are synthesized under the near-surface region of the Nd:Y3Al5O12 (Nd:YAG) crystal by direct Cu+ ions implantation. Subsequently, the monolithic ridge waveguide with embedded Cu NPs is fabricated by C4+ ions irradiation and diamond saw dicing. The nonlinear optical response of the sample is investigated by the Z-scan technique, and pronounced saturable absorption is observed at the 1030 nm femtosecond laser. Based on the obvious saturable absorption of Cu NPs embedded Nd:YAG crystal, 1 μm monolithic mode-locked pulsed waveguide laser is implemented by evanescent field interaction between NPs and waveguide modes, reaching the pulse duration of 24.8 ps and repetition rate of 7.8 GHz. The work combines waveguides with NPs, achieving pulsed laser devices based on monolithic waveguide chips.
High-performance ultra-compact polarization splitter-rotators (PSRs) are designed and experimentally demonstrated, using dual etching and a tapered asymmetrical directional coupler. First, two novel PSRs are designed with nanowire and subwavelength grating cross-port waveguides and verified in simulations. Then, one of the two PSRs is fabricated. Experiment results reveal that the extinction ratio is higher than 28 dB or 32 dB at 1550 nm for the launched fundamental transverse magnetic or the transverse electric modes, while the corresponding insertion loss and polarization conversion loss are 0.33 dB and 0.18 dB, respectively.
We demonstrate a polarization-insensitive silicon 4×4 optical switch based on Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) switch elements. On-chip polarization controllers are integrated before the switch fabric to automatically adjust an arbitrary input polarization to the transverse electric mode. The 4×4 switch fabric is based on a dilated double-layer network architecture to completely cancel the first-order crosstalk. Thermo-optic phase shifters are integrated in the MZI switch elements and the polarization controllers for adjustment of the switching state and polarization, respectively. We develop a polarization control algorithm based on a gradient descent method for automated polarization control. The polarization recovery time is less than 4 ms, and the measured polarization-dependent loss is ∼2 dB. The scheme provides a new solution for realizing polarization-insensitive silicon optical switches.
A micro stereo sensor system is proposed for human sensors, where eyes, ears, tongue, nose, body, and brain are applied by six panda rings embedded in a Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI). The input power is applied to the upper branch of MZI and propagates within the system. The six antennas (sensors) are formed by the whispering gallery modes of the panda rings. The space–time modulation signal is applied to the MZI lower branch. The modulated stereo signals can be configured as the plasmon (electron) spin orientations, which can be identified and applied for quantum codes and quantum consciousness.
The research on nanophotonic devices has made great progress during the past decades. It is the unremitting pursuit of researchers that realize various device functions to meet practical applications. However, most of the traditional methods rely on human experience and physical inspiration for structural design and parameter optimization, which usually require a lot of resources, and the performance of the designed device is limited. Intelligent algorithms, which are composed of rich optimized algorithms, show a vigorous development trend in the field of nanophotonic devices in recent years. The design of nanophotonic devices by intelligent algorithms can break the restrictions of traditional methods and predict novel configurations, which is universal and efficient for different materials, different structures, different modes, different wavelengths, etc. In this review, intelligent algorithms for designing nanophotonic devices are introduced from their concepts to their applications, including deep learning methods, the gradient-based inverse design method, swarm intelligence algorithms, individual inspired algorithms, and some other algorithms. The design principle based on intelligent algorithms and the design of typical new nanophotonic devices are reviewed. Intelligent algorithms can play an important role in designing complex functions and improving the performances of nanophotonic devices, which provide new avenues for the realization of photonic chips.
An equivalent circuit model including multi-section distributed parameters is proposed to analyze wideband photodiodes (PDs) with coplanar waveguide (CPW) electrodes. The model helps extract CPW parameters as well as intrinsic bandwidth parameters so that the influence of the CPW structure can be investigated, making it valuable for the design of high-performance PDs. PDs with an inductive 115 Ω impedance CPW are fabricated, and the 3 dB bandwidth is improved from 28 GHz to 37.5 GHz compared with PDs with a conventional 50 Ω impedance CPW.
Photonic waveguide arrays provide a simple and versatile platform for simulating conventional topological systems. Here, we investigate a novel one-dimensional (1D) topological band structure, a dimer chain, consisting of silicon waveguides with alternating self-coupling and inter-coupling. Coupled mode theory is used to study topological features of such a model. It is found that topological invariants of our proposed model are described by the global Berry phase instead of the Berry phase of the upper or lower energy band, which is commonly used in the 1D topological models such as the Su–Schrieffer–Heeger model. Next, we design an array configuration composed of two dimer patterns with different global Berry phases to realize the topologically protected waveguiding. The topologically protected propagation feature is simulated based on the finite-difference time-domain method and then observed in the experiment. Our results provide an in-depth understanding of the dynamics of the topological defect state in a 1D silicon waveguide array, and may provide different routes for on-chip lightwave shaping and routing.
We propose and analyze a silicon hybrid plasmonic polarization splitter-rotator with an ultra-short footprint using an asymmetric bent directional coupler on a silicon-on-insulator platform. Benefitting from the large birefringence induced by the bent structure and plasmonic effect, the cross-polarization coupling length is only 5.21 μm. The transverse magnetic to transverse electric polarization conversion efficiency is over 99.9%, with an extinction ratio of 20.6 dB (32.5 dB) for the transverse magnetic (transverse electric) mode at 1.55 μm. Furthermore, the polarization conversion efficiency is higher than 90% while maintaining cross talk below ?19 dB within the bandwidth of 80 nm.
We report an 8-channel wavelength-mode optical pulse interleaver on a silicon photonic chip. Wavelength- and mode-division multiplexing techniques are combined to increase the repetition rate of the pulses without adding the complexity of a single dimension. The interleaver uses a cascaded Mach–Zehnder interferometer architecture as a wavelength-division (de)multiplexer, an asymmetric directional coupler as a mode (de)multiplexer, and various lengths of silicon waveguides as delay lines. A pulse sequence with a time interval of 125 ps is implemented with the repetition rate being eight times that of the initial one. The demonstrated wavelength-mode multiplexing approach opens a new route for the generation of high-speed optical pulses.
In this Letter, we reported the preliminary results of an integrating periodically capacitive-loaded traveling wave electrode (CL-TWE) Mach–Zehnder modulator (MZM) based on InP-based multiple quantum well (MQW) optical waveguides. The device configuration mainly includes an optical Mach–Zehnder interferometer, a direct current electrode, two phase electrodes, and a CL-TWE consisting of a U electrode and an I electrode. The modulator was fabricated on a 3 in. InP epitaxial wafer by standard photolithography, inductively coupled plasma dry etching, wet etching, electroplating, etc. Measurement results show that the MZM exhibits a 3 dB electro-optic bandwidth of about 31 GHz, a Vπ of 3 V, and an extinction ratio of about 20 dB.
An integrated optoelectronic chip pair, which can transmit and receive optical signals simultaneously, is proposed in this Letter. The design and optimization of its key structure, the vertical cavity surface emitting laser’s distributed Bragg reflector, are presented. Analysis is also done for its influence on the integrated chip’s performance. Moreover, the chip pair’s performance under dynamic conditions is analyzed. Their 3 dB modulation bandwidths are higher than 10 GHz, and their 3 dB photo-response bandwidths are around 23 GHz. Their applications will further improve the performances of the optical interconnects.
Wide-range optical sensors based on a single ring resonator are investigated theoretically and experimentally. The sensor worked at the TE and TM modes simultaneously. Because the sensitivities of the TE mode and TM mode are different, the TE mode is used for the large measurement range, and the TM mode is used for the high sensitivity measurement. The experimental results showed that the measurement range for the TE mode was almost three times larger than that of the TM mode. A sensitivity of 233 nm/RIU was achieved for the wavelength interrogation of the TM mode.
In this Letter, a pair of integrated optoelectronic transceiving chips is proposed. They are constructed by integrating a vertical cavity surface emitting laser unit above a positive-intrinsic-negative photodetector unit. One of the transceiving chips emits light at the wavelength of 848.1 nm with a threshold current of 0.8 mA and a slope efficiency of 0.81 W/A. It receives light between 801 and 814 nm with a quantum efficiency of higher than 70%. On its counterpart, the other one of the transceiving chips emits light at the wavelength of 805.3 nm with a threshold current of 1.1 mA and a slope efficiency of 0.86 W/A. It receives light between 838 and 855 nm with a quantum efficiency of higher than 70%. The proposed pair of integrated optoelectronic transceiving chips can work full-duplex with each other, and they can be applied to single fiber bidirectional optical interconnects.
The fabrication and characterization of p-i-n photodiodes integrated with wide spectrum focusing reflectors using nonperiodic strip and concentric-circular subwavelength gratings are presented. The experimental results show that the gratings can reflect and focus the incident light on the absorber of the photodiode, and thus can simultaneously achieve high speed and high efficiency. For the gratings’ integrated photodiodes, the responsivity is improved over a wide spectral range, and when the absorber was 600 nm and the mesa diameter was 40 μm, a responsivity of 0.46 A/W at a wavelength of 1.55 μm and a 3 dB bandwidth of 21.6 GHz under a reverse bias of 3 V were simultaneously obtained.
Optical delay lines (ODLs) are one of the key enabling components in photonic integrated circuits and systems. They are widely used in time-division multiplexing, optical signal synchronization and buffering, microwave signal processing, beam forming and steering, etc. The development of integrated photonics pushes forward the miniaturization of ODLs, offering improved performances in terms of stability, tuning speed, and power consumption. The integrated ODLs can be implemented using various structures, such as single or coupled resonators, gratings, photonic crystals, multi-path switchable structures, and recirculating loop structures. The delay tuning in ODLs is enabled by either changing the group refractive index of the waveguide or changing the length of the optical path. This paper reviews the recent development of integrated ODLs with a focus on their abundant applications and flexible implementations. The challenges and potentials of each type of ODLs are pointed out.
In this Letter, the effects of material/structure parameters of photonic crystal (PhC) parallel waveguides on the coupling length are investigated. The results show that, increasing the effective relative permittivity of the PhC leads to a downward shift of the photonic bandgap and a variation of the coupling length. A compact PhC 1.31/1.55 μm wavelength division multiplexer (WDM)/demultiplexer with simple structure is proposed, where the output power ratios are more than 24 dB. This WDM can multiplex/demultiplex other light waves efficiently.
We demonstrate a polarization insensitive arrayed-input spectrometer using echelle diffraction grating (EDG) for hyperspectral imaging. The EDG consists of 65 input waveguides and 129 output waveguides, allowing spectral measurements of 65 image pixels at a time when used in combination with a micro-electromechanical system micro mirror array. The spectral resolution reaches 7.8 nm for wavelengths ranging from 1250 to 1700 nm. The measured loss is 2 dB, and the crosstalk is lower than 20 dB. The 3 μm silicon-on-insulator platform provides the device with polarization insensitive characteristics. The chip size is only 6 mm×10 mm.
We experimentally observe that Si micro-ring modulator (MRM) modulation characteristics are strongly influenced by the modulation data rate and the data pattern and determine this influence is due to the temperature increase caused by dynamic power dissipation within the Si MRM device. We also quantitatively determine the amount of Si MRM resonance wavelength shift due to different modulation data rates, data patterns, and modulation voltages. Our results should be of great help for achieving reliable and optimal modulation characteristics for Si MRMs.
In this Letter, we demonstrate a 1×4 low-crosstalk silicon photonics cascaded arrayed waveguide grating, which is fabricated on a silicon-on-insulator wafer with a 220-nm-thick top silicon layer and a 2 μm buried oxide layer. The measured on-chip transmission loss of this cascaded arrayed waveguide grating is ~4.0 dB, and the fiber-to-waveguide coupling loss is 1.8 dB/facet. The measured channel spacing is 6.4 nm. The adjacent crosstalk by characterization is very low, only 33.2 dB. Compared to the normal single silicon photonics arrayed waveguide grating with a crosstalk of ~ 12.5 dB, the crosstalk of more than 20 dB is dramatically improved in this cascaded device.
We present in this work a new mathematical model to analyze and evaluate optical phenomena occurring in the nonuniform optical waveguide used in integrated optics as an optical coupler. By introducing some modifications to the intrinsic integral, we perfectly assess the radiation field present in the adjacent medium of the waveguide and, thus, follow the evolution of the optical coupling from the taper thin film to the substrate and cladding until there is a total energy transfer. The new model that is introduced can be used to evaluate electromagnetic field distribution in three mediums that constitute any nonuniform optical couplers presenting great or low wedge angles.
An ultra-broadband and fabrication-tolerant silicon polarization rotator splitter is proposed in this Letter. Benefitting from the broadband and low-loss characteristics of the bi-level taper and counter-tapered coupler, the designed device has a simulated insertion loss and crosstalk of less than 0.2 and 15 dB in the waveband from 1290 to 1610 nm. These characteristics make it valuable in applications with large bandwidth requirements, such as full-grid Coarse wavelength division multiplexer (CWDM) and diplexer/triplexer fiber-to-the-home systems. The fabrication tolerance of the design is also analyzed, showing that the device performance is quite stable with normal manufacturing errors in silicon photonics foundries.
A multichannel polarization-entangled photon-pair source in an MgO-doped periodically poled lithium niobate (MgO:PPLN) waveguide is proposed. Based on type I quasi-phase-matched spontaneous parametric down conversion in a single MgO: PPLN waveguide placed inside a Sagnac interferometer and pumped by monochromatic light, a source capable of supporting tens to hundreds of channels of polarization-entangled photon pairs in fiber communication bands simultaneously can be achieved. An inherent channel switch of this source is investigated, which will be significant for future entanglement distribution networks.
We propose an ultra-broadband and fabrication-tolerant polarization rotator-splitter (PRS) based on a waveguide with an L-shaped cross section and a Y-junction. The proposed PRS is based on the 220 nm silicon-on-insulator platform, and it shows less than 0.27 dB insertion losses and larger than 14 dB polarization extinction ratios over a wavelength range from 1200 to 1700 nm. To the best of our knowledge, the PRS working in the whole optical communication band is proposed for the first time.
We propose and demonstrate an ultrasensitive integrated photonic current sensor that incorporates a silicon-based single-mode-multimode-single-mode waveguide (SMSW) structure. This kind of SMSW structure is placed over a direct current carrying power resistor, which produces Joule’s heat to change the temperature of the SMSW and further results in the change of the effective refractive index between different propagating modes. Interference occurs when the modes recombine at the second single mode waveguide. Finally, the current variation is measured by monitoring the shift in the output spectrum of the multimode interferometer. In low current, the wavelength shift has almost linear dependence: Δλ∝Ic. This effect can be used as a current sensor with a slope efficiency of 4.24 nm/A in the range of 0–200 mA.
A system of an add-drop microring resonator integrated with a sampled grating distributed feedback (SG-DFB) is investigated via modeling and simulation with the time-domain traveling wave (TDTW) method. The proposed microring resonator comprises a SiO2 waveguide integrated with an InGaAsP/InP SG-DFB, and the SiO2 waveguide consists of a silicon core having a refractive index of 3.48 and Kerr coefficient of 4.5×10 18 m2/W. The SG-DFB consists of a series of grating bursts that are constructed using a periodic apodization function with a burst spacing in the grating of 45 μm, a burst length of 5 μm, and 10 bursts across the total length of the SG-DBR. Transmission results of the through and drop port of the microring resonator show the significant capacity enhancement of the generated center wavelengths. The Q-factor of the microring resonator system, defined as the center wavelength (λ0) divided by 3 dB FWHM, without and with integration with the SG-DFB is calculated as 1.93×105 and 2.87×105, respectively. Analysis of the dispersion of the system reveals that increasing the wavelength results in a decrease of the dispersion. The higher capacity and efficiency are the advantages of integrating the microring resonator and the InGaAsP/InP SG-DFB.
An integrated, tunable spectrometer based on a silicon-on-sapphire platform is designed at wavelengths of 2.29–2.35 μm. Its pivotal component is a 4.7 μm-radius ring resonator on a graphene monolayer. Its full width at half-maximum and free spectral range are ~1.5 and ~45 nm, respectively, as found through a numerical simulation and theoretical computation. Sixteen characteristic peaks are obtained by tuning the Fermi level of graphene. The gap between the ring and waveguides is increased by 0.5 μm to increase the resolution, and though this can drastically reduce the transmission rate, an upper sapphire layer maintains light to the drop port.
Definitions of mode-field half-width and divergence half-angle according to different kinds of methods are analyzed in this work. Numerical results of these definitions are given for the fundamental mode and suggest that some of them are more suitable for describing the transmission characteristics of a slab waveguide.
We propose a Y-type polarization beam splitter based on internal polarization-selective defects within crystal waveguides in a two-dimensional square-lattice photonic crystal with solid rods. When the nonpolarized light launches from the input port, different polarizations will be separated and can only transmit through their own channel. It is demonstrated by finite element method that the proposed structure can achieve good performance for both the transverse electric and transverse magnetic polarizations in a wide range of wavelength, with the polarization extinction ratio more than 25 dB, the degree of polarization nearly 1, and the insert loss less than 0.5 dB, respectively.
In order to realize homodyne reception and Doppler frequency shift tracking in ground-to-satellite coherent laser communication, a local laser is experimentally demonstrated in this Letter. It is realized based on modulation-sideband injection locking, and has a 10 GHz tuning range, a 1 THz/s tuning rate, a 5 kHz linewidth, and 16 mW of output power. When applied to a Costas loop in a coherent laser communication system, the local laser can achieve ±5 GHz Doppler frequency shift tracking with a 20 MHz/s frequency shift rate, which is sufficient for the ground-to-satellite coherent laser communication.
A novel and simple polarization independent grating couplers is designed and analyzed here, in which the TE polarization and the TM polarization light can be simultaneously coupled into a silicon waveguide along the same direction with high coupling efficiency. For the polarization-insensitive grating coupler, the coupling efficiencies of two orthogonal polarizations light are more than 60% at 1550 nm wavelength based on our optimized design parameters including grating period, etching height, filling factor, and so on. For TE mode the maximum efficiency is ~72% with more than 30 nm 1 dB bandwidth, simultaneously, for TM mode the maximum efficiency is 75.15% with 40 nm 1 dB bandwidth. Their corresponding wavelength difference between two polarizations’ coupling peaks is demonstrated to be 35 nm. Polarization independent grating coupler designed here can be widely used in optical communication and optical information processing.
We report the fabrication details of a monolithically integrated electro-absorption modulated distributed feedback laser (EML) based on the ion-implantation induced quantum well intermixing (QWI) technique. To well-preserve material quality in the laser region, thermal-oxide SiO2 is deposited before implantation and the ion-implantation buffer layer is etched before annealing. Thirteen pairs quantum well and barrier are employed to compensate deterioration of the modulator’s extinction ratio (ER) caused by the QWI process. The fabricated EML exhibits an 18 dB static ER at 5 V reverse bias. The 3 dB small signal modulation bandwidth of modulator is over 13.5 GHz indicating that this EML is a suitable light source for over 16 Gb/s optical transmission links.
We report a compact 2×2 Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) electro-optic switch fabricated on a silicon-on-insulator using standard complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) processes. With a short modulation arm length of 200 μm, the crosstalk is reduced to 22 dB by the new modulation scheme of push–pull modulation with a pre-biased π/2 phase shift. The new modulation scheme can also work with a fast switching time of about 5.4 ns.
We present a compact displacement measurement system possessing the capability of nanometer-scale precision. On basis of integrating single grating with 3×3 coupler for phase shift in interference signal, the present scheme features advantages of simple structure, convenient alignment, and insensitivity to air turbulence. Linear comparisons between our system and HP5530 show a residual error less than 81 nm during step motions along a 10 mm round-trip, and a discrepancy less than 15 nm in the case of 200 μm movement. We also demonstrate a measurement stability test in a duration of 300 s, which shows the proposed scheme potentially performs better than HP5530 in terms of long-term stability.
A tunable dual-band infrared polarization filter is proposed and investigated. Based on the perfect absorption characteristic of the metal-dielectric-metal sandwich structure, the reflection spectrum performs as a filter. The filter consists of three layers. The top layer is a compound metal nano-structure array comprised of rectangular strips. The middle and bottom layers are a dielectric spacer and metal film, respectively. The calculated results show that the filter properties are closely related to the polarization of the incident light. Different dual-band wavelengths are filtered while the incident light has different polarizations, which are parallel or vertical to the x axis. Moreover, it is found that the resonant wavelength strongly depends on the length of the rectangular strip (which causes the resonant effect) and is independent of other strips. Therefore, the filter wavelengths can be tuned freely by adjusting the length of the corresponding rectangular strip. In addition, the calculated results show that all of the intensities at the filter wavelengths are closed to zero, which implies that the filter exhibits good filtering performance.
In this Letter, we study the characteristics of a selectively buried glass waveguide that is fabricated by the backside masking method. The results show that the surface region appears when the width of the backside mask is larger than 7 mm. Here, the glass substrate is 1.5 mm thick. It is also found that the buried depth evolution of the transition region remains almost unchanged and is independent of the width of the backside mask. The loss of the transition region is only 0.28 dB at the wavelength of 1.55 μm if the surface condition is good enough.
We demonstrate a large-mode-volume transverse-electric-polarized λ/4 shifted distributed feedback (DFB) cavity on silicon-on-insulator (SOI). A 2.86 mm-long DFB cavity with sidewall corrugation on the ridge is fabricated on a silicon rib waveguide. The cavity structure is designed to enlarge both the longitudinal and transversal mode profiles of the cavity to enclose more luminescent media. Design strategies are verified by both finite difference time domain simulation and experiments. A linewidth of 69 pm and an extinction ratio of 15 dB is obtained, indicating not only the well confinement of the longitudinal mode, but also its well stretching to the cavity ends. The mode volume is 75.39 μm3.
Combination of full-vector finite element method with anisotropic perfectly matched layers results in a novel structure of low-dispersion photonic crystal fiber with high birefringence. The negative dispersion can be obtained at a wavelength of 1.55 μm by adjusting the lattice constant Λ and the round air hole diameter d. Numerical results show that the dispersion variation is negative in the C band, the dispersion slope values are between 0.112 and 0.142 ps·km-1·nm-2 over the C band, and the birefringence is 5.7×10-3.
In present work, we demonstrate that when a transverse magnetic (TM) Gaussian beam is incident to a magnetic metamaterial (MM) slab, it can be completely absorbed at a particular direction, resulting in a unidirectional perfect absorption. The unidirectionality is due to the time reversal symmetry (TRS) breaking nature of the MM; while the perfect absorbing effect is explained by the multiple scattering theory and the effective medium theory. By tuning the magnitude and the orientation of the external magnetic field, the working frequency can be adjusted and the unidirectionality can be reversed. Accordingly, we can design tunable compact optical devices to achieve unidirectional perfect absorption.
A rigorous supermode solution method in a strong absorption slab multilayer waveguide is performed. The method is directed toward finding solutions for a sophisticated complex determinant in a complex plane. The rigorous results are applied to design a waveguide photodetector that has a configuration of a vertical directional coupler. Absorption lengths of the supermodes and coupling length of the coupler are calculated based on an effective index approach by using the rigorous results of the strong absorption slab multilayer waveguide to optimize the directional coupling waveguide photodetector.
A novel inorganic-organic hybrid polymer polysiloxane-liquid (PSQ-L) is introduced for defining waveguides. The PSQ-L polymer film shows good optical properties and high thermal stability. The all polymer microring resonator is fabricated by conventional lithography and ICP etching process. About 3-dB extinction ratio from the through port and 23-dB extinction ratio from the drop port are obtained. A high Q value of 5.7×104 is obtained. The optical loss of the bending waveguides is estimated to be 1.6 dB/cm. The high Q polymer ring resonators show potential in sensing applications.
Modal filtering in nulling interferometer is based on the capability of single-mode waveguides to transmit only one complex amplitude function to eliminate virtually any perturbation of the interfering wavefronts. In this letter, we focus on realizing single-mode waveguide of chalcogenide glasses in the thermal infrared range 6–20 \mu m by burying a GASIR (Ge-As-Se) fiber core in the substrates of As-Se-S glasses system. To match the single-mode operation, GASIR fiber core of about 15-μm diameter is drawn, the fiber core is buried into As-Se-S substrates by heating two kinds of glasses to a suitable temperature. The propagation mode is tested by guiding a CO2 laser emitting at 9.3 μm into the waveguide. Single-mode out coming signal is obtained by an infrared camera.
Through finding the derivatives of the group delay and transmittance of the coupled double-ring resonators (CDRRs) with respect to different structure parameters, the dispersion and filtering characteristics of CDRRs varying with different coupling and attenuation/gain coefficients are analyzed systematically. The parameter ranges in that obvious slow and fast light can be achieved are given, and large light delay and advancement without serious attenuation and great distortion are obtained.
The optical characteristics of the magnetic metamaterial (MM) composed of the ferrite rods are theoretically investigated. Firstly, a photonic band-gap (PBG) resulting from the magnetic surface plasmon (MSP) resonance is recognized by observing the photonic band structure. Moreover, the PBG can be manipulated flexibly by using an external magnetic field (EMF). In particular, the effect is very roust against structural perturbations, which can be corroborated by examining the transmittances for a MM slab with different position disorders and size fluctuations. Based on this peculiar property, we design an electromagnetic switch with fast response, which is demonstrated by calculating the electric field patterns of a Gaussian beam incident on a MM slab.
A novel design of multimode light power splitter is proposed and fabricated by using secondary asymmetric Y branches. An almost equally divided output among output terminals is obtained experimentally. Maskless laser direct writing technique is applied in the fabrication process to facilitate the formation of power splitters by ultraviolet curable polymer. The analysis of the performances of both four-port and eight-port devices shows that these two dividers obtain a power splitting uniformity of more than 95%.
A photonic approach for measuring microwave frequency over a wide bandwidth is proposed. An optic group delay line composed of several magneto-optical switches and a 1.6-km single-mode fiber is used as a tunable dispersive medium in the measurement setup. A minimum frequency accuracy of 80 MHz in the range of 1–20 GHz is achieved experimentally.